What is SCADA System
The word SCADA means “Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition”. The definition clearly explains what are the functions and objectives of a SCADA system, namely supervision, control and data acquisition.
A SCADA system is part of an architecture that includes:
- One or more computers, connected to each other, that perform the supervisory functions and implement the human-machine interface (HMI)
- A series of peripheral devices (RTUs, i/o Modules, PLCs) that interface to the process (machinery, plant, etc.) through sensors and actuators
- A communication network, with a variety of transmission media and communication protocols, able to ensure the correct exchange of data between peripheral devices and supervisory computers
A SCADA software is an integrated development environment, which provides all the tools necessary to create SCADA applications, designed to run on supervisory computers and perform the functions that are typical of a SCADA system: supervision, control and data acquisition.
SCADA TUTORIALSSupervision
Supervision is the function that allows the operator to have an immediate view of the process status and to control how the process evolves over time by analyzing the sequence of operating states.
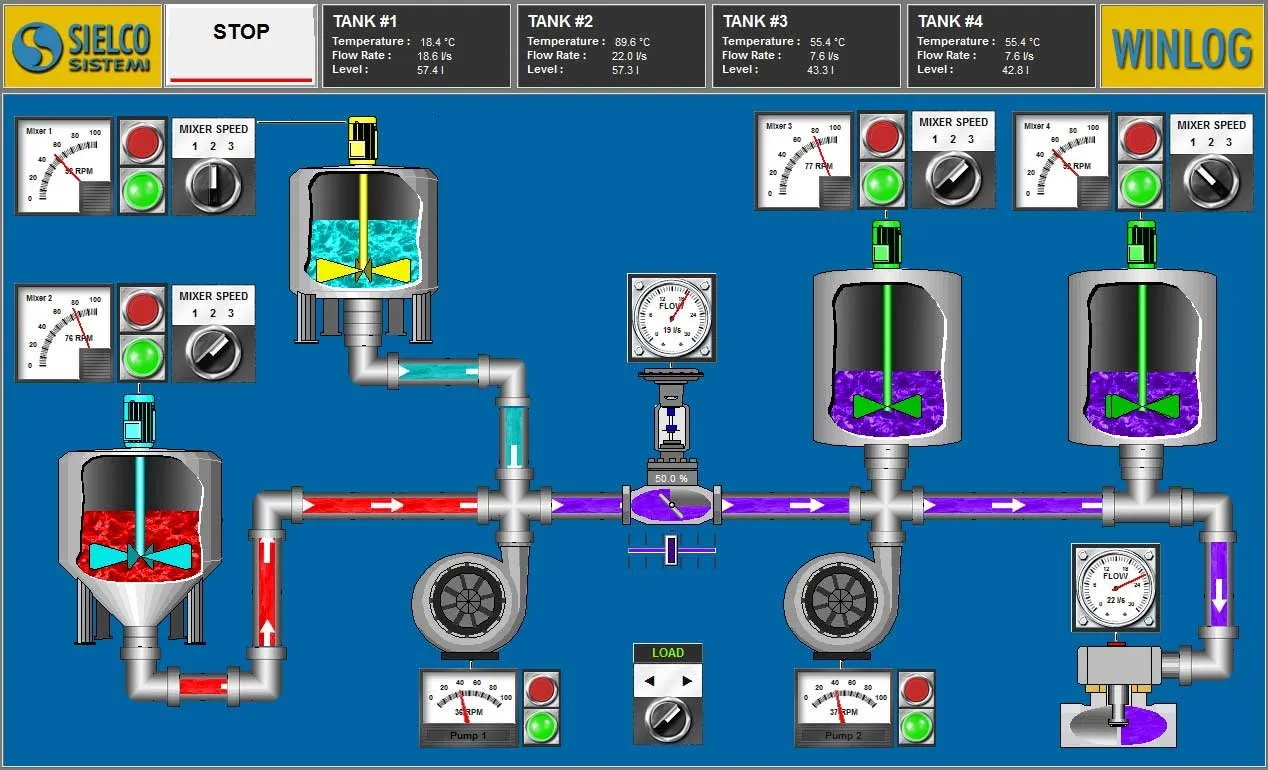
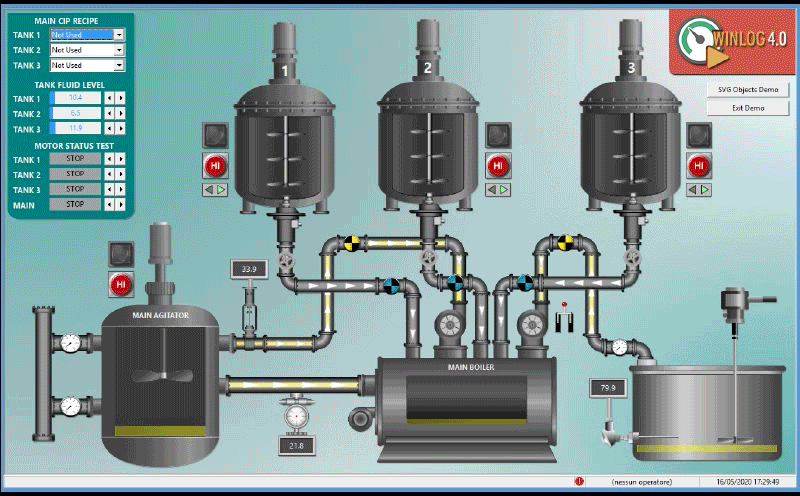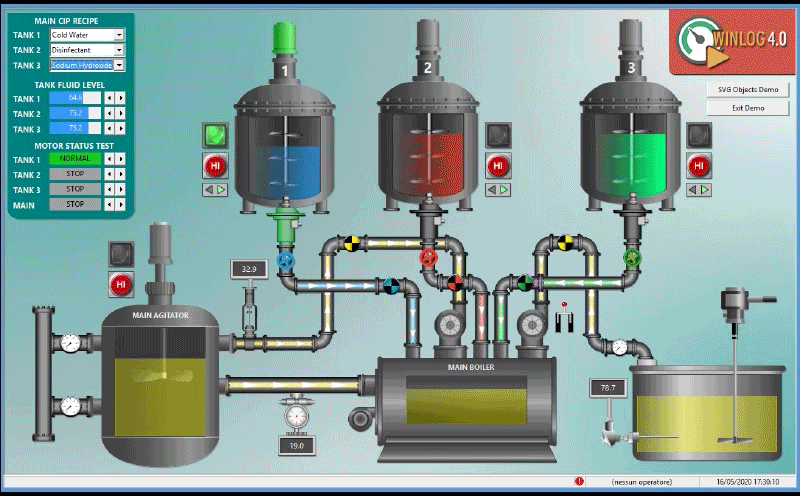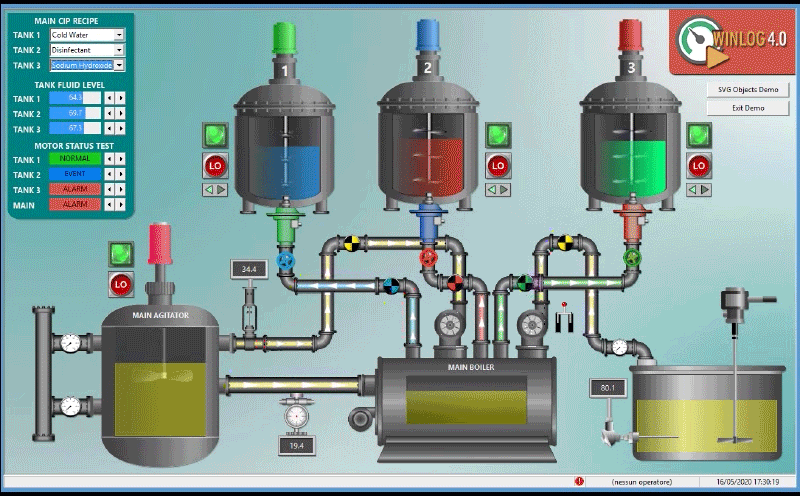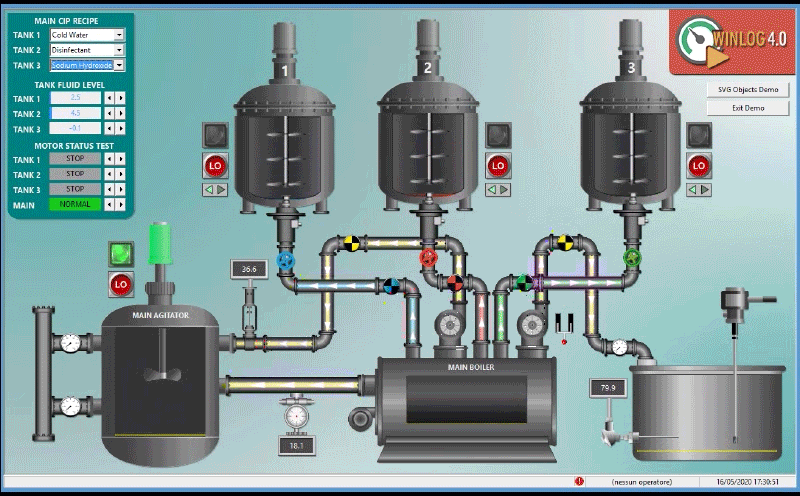
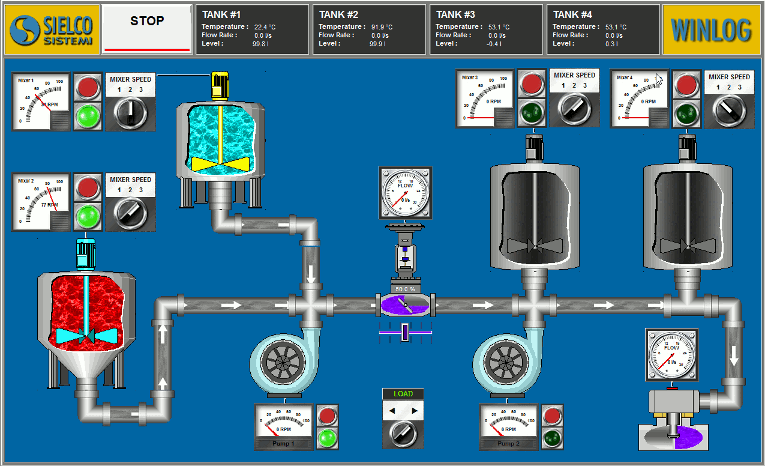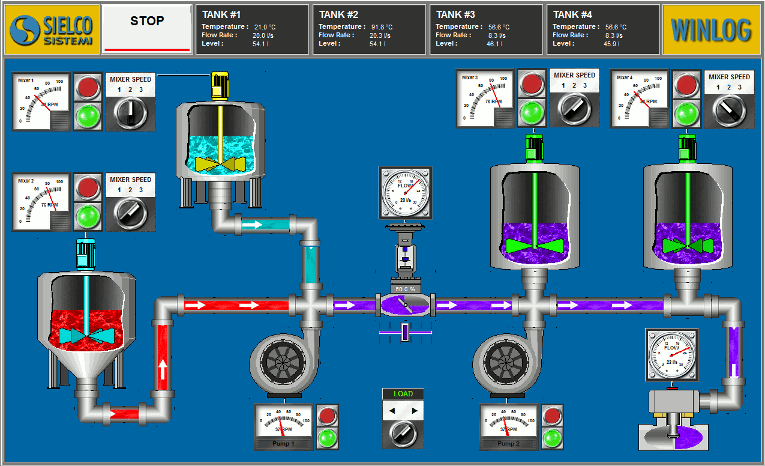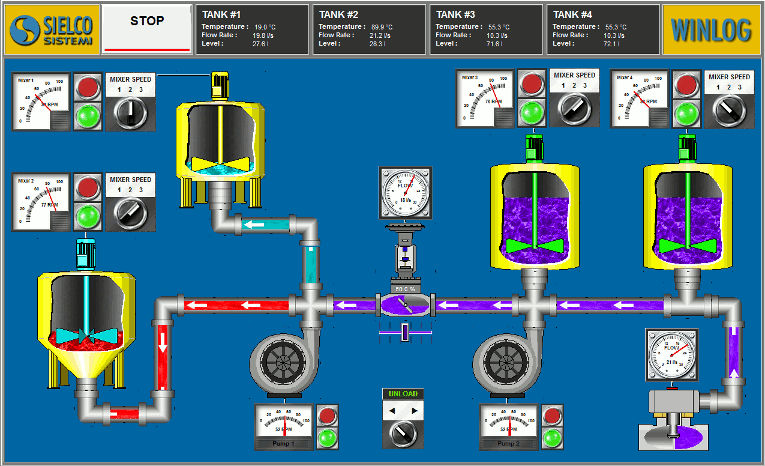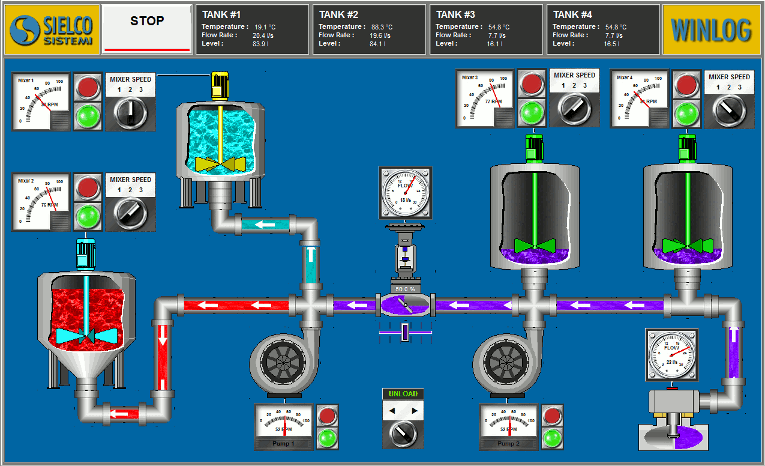
The main task of the supervision is to realize the human-machine interface (HMI). To be effective, the HMI must provide the operator with a prompt and complete image of the whole process, highlighting the status, the evolution and the unexpected deviations (alarms).
For an effective HMI, the graphic representation is of great importance, since it translates information relevant to the process into a visual language of easy understanding for the operator.
For example, you can display the status of a pump through a graphic symbol with different colors, the change of the value of a pressure through a graphical trend, the occurrence of an alarm through a pop-up window.
More infoControl
The control function of a SCADA system consists in the ability of the control system to interact with the controlled process, in order to modify its evolution according to pre-established rules or decisions taken by the operator.
It is important to underline that, with “control of a SCADA system, we do not mean “real time process control”, usually the prerogative of the PLC, but rather the ability to modify the evolution of the process, for example by sending a different work recipe.
To better clarify the concept, we can say that, with reference to a particular process temperature, the task of a real time control is to keep this temperature unchanged (by acting on the appropriate actuators), while the task of the SCADA control is to fix the temperature at which the process should work (by sending the appropriate set point).
Data Acquisition
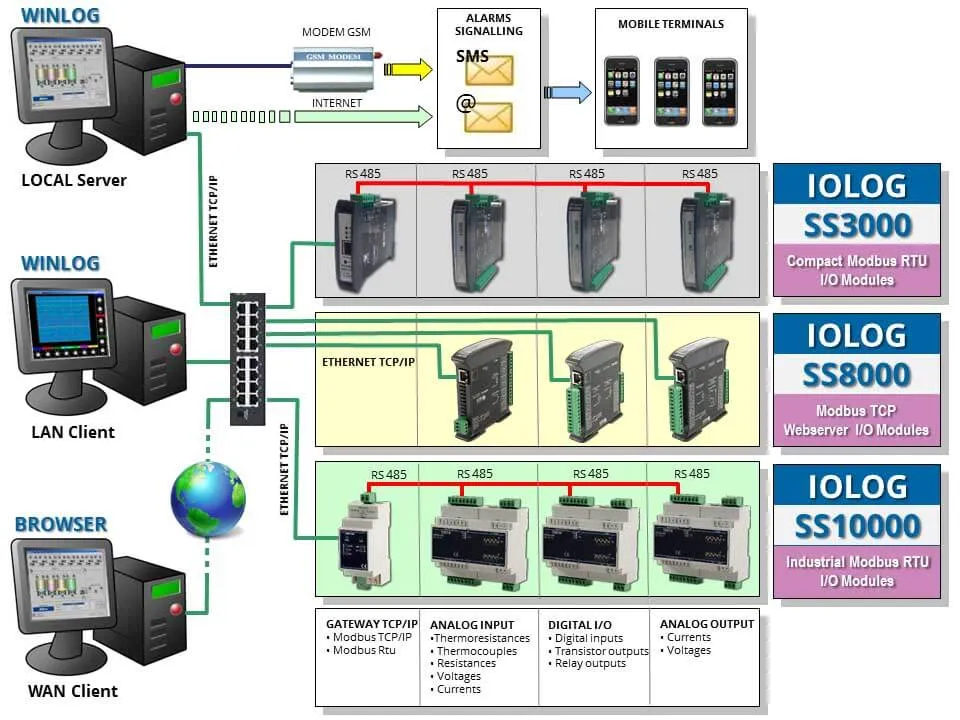
Data acquisition not only means transfer of information from peripheral devices to supervisory computers, but also transfer of information in the opposite direction, in order to allow the supervisory system to control the process, that is to direct its evolution by modifying the values of the variables that condition its operation.
We can say that data acquisition is the main function among those performed by SCADA systems. In fact, by putting the process in communication with the supervision, data acquisition makes it possible for the supervisory system to get all the information on the process status that are necessary to allow the observation of the process itself.
The task of data acquisition is to ensure the error-free transfer of information between process and supervision, in a context characterized by a variety of transmission media and different communication protocols.
More infoWhat is SCADA Software

SCADA software is an integrated development environement which allows creation of SCADA HMI applications. Several SCADA software from various manufacturers are available, with significant differences in price and performance. The choice of the SCADA software most suitable for the application to be developed depends on several factors, as well as personal preferences, but is generally based on the complexity of the project, the required performances, any constraints imposed by the client and the available budget.
You should also consider the learning time, which is usually higher in case of a more complex SCADA software. As a general rule, the choice of a complex SCADA software is justified when the project involves a large and high-cost plant, for which software cost and learning time are no longer relevant. in the case of small-to-medium projects with a limited budget, it is advisable to move towards SCADA software that have a lower cost and require a shorter learning time.
All SCADA software, regardless of complexity, must however have common features regarding the following topics:
- Communication: a set of development tools and communication drivers to interface with most of electronic devices (PLCs, controllers, meters, etc.) from various manufacturesrs operating in the Industrial Automation market. It allows to build the DB of the variables to be exchanged with external devices and includes the most common communication protocols such as OPC, Siemens, Omron, Allen Bradley, Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, KNX, Bacnet, etc.
- Human Machine Interface (HMI): a set of development tools and graphic libraries to create static and animated templates. It is important to underline the importance of graphics in the development of a SCADA application. The human-machine interface (HMI) is in fact all the more effective, the more it is able to provide the operator with a prompt and complete image of the whole process, highlighting the status, the evolution and the unexpected deviations (alarms).
- Process information: a set of development tools to allow the operator to have all the information describing the current status of the process (online data) and its evolution over time (historical data). For example, to allow the operator to be promptly notified in case of malfunction or to analyze the graphical trends of the monitored and recorded process variables.
- Reports: a set of development tools to sort and process the information acquired from the process in order to generate reports for production and quality managers. Reports usually refer to a specific production batch, highlighting its characteristics and certifying its compliance with the requirements.
- Architecture: a set of tools and rules to build complex architectures in case of multiple applications interacting with each other through local (LAN) or public (Internet) networks and able to interface with multiple operators both local and remote (via browser)
Advantages of SCADA Software

SCADA applications are used today in most industrial fields and are an indispensable aid for all companies, regardless of size and sector of activity. SCADA software is the most suitable development environment for the easy and intuitive creation of complex SCADA applications.
SCADA applications provide several benefits, but having to highlight one in particular, we can say that they replace the man in carrying out many routine and tedious tasks, which increases productivity, provides a faster management of alarms and reduces the risk of potentially dangerous situations for the environment. More generally, we can say that SCADA applications:
- Provide a large amount of information. All system status information, both acquired from the field sensors and provided by real-time control devices (PLC), is collected, saved and made available for further processing, aimed at quality control, efficiency gain and production optimization
- Provide a synthetic and clear picture of the production plant. A series of templates, that are part of the human-machine interface (HMI), provide the operator with a graphical picture of the whole process, its evolution over time and the unexpected deviations (alarms). By this way all information relevant to the process are translated into a visual language of easy understanding for the operator.
- Can grow and adapt easily to the growth of the company. The modular and flexible structure of SCADA software makes it possible to adapt to the different situations that arise when the company needs to grow or change, to respond to the challenges of a globalized market. The SCADA software includes, for example, all the development tools that allow to modify the SCADA application in order to provide communication with new devices, in a context characterized by a variety of transmission media and different communication protocols.
- Allow centralized control of remote units. Many companies, especially those that manage public service networks (water, electricity, etc.), are characterized by a structure distributed throughout the territory, which traditionally requires the fixed or programmed presence of technical staff for operation and maintenance. The SCADA application ensures remote control of peripheral units and allows technical staff to access all information with a simple browser.
Types of SCADA Software


A first difference concerns the type of software platform:
- Dedicated platforms, consisting of software developed “ad hoc” to supervise a particular machine or a particular plant. They can be developed by the same manufacturer which also supplies the machine to be supervised or by a software house on the basis of specifications provided by the customer to carry out, for example, the supervision of a plant. Even if the operator has the possibility to modify the configuration parameters and the process recipes, this supervisory software finds its main limitation in the impossibility of growing or adapting to the different conditions of use not initially foreseen.
- Open platforms, consisting of software that provides the user with an integrated development environment for creating SCADA applications, i.e. making available the tools necessary to manage the typical functions of a SCADA application (protocols for communicating with field devices, graphics libraries for creating templates, etc.). In this case the software is structured in two levels: a first level, common to all users, consisting of the SCADA platform and a second level, typical of the machine or plant to be supervised, consisting of the SCADA application created by the user. The big advantage of the open platform over the closed platform is that it gives the user total freedom to expand or modify the project.
A second difference concerns the architecture of the SCADA system:
- System consisting of a single supervisory PC connected to the field devices. It is the most common case, which is not necessarily the simplest. You can have very complex SCADA systems, with several plants to be supervised, which are distributed over geographical areas distant from each other; just as the complexity of the system is affected by the number of variables to manage (from a few units to tens of thousands of tags), the variety of connected field devices, the different communication protocols. In the simplest cases, when the SCADA system consists of a single PC connected to a single machine (usually controlled by a single PLC), we also speak of SCADA-HMI.
- Systems made up of multiple supervisory PCs connected to each other via a local network (LAN) or public network (Internet) and distributed on multiple hierarchical levels. The most common system is characterized by multiple PCs at the same hierarchical level connected to a central PC; second-level PCs differ on the basis of geographical characteristics (each PC belongs to a different geographical area) or functional (each PC manages a particular function); the central PC makes all the information available from a single location.
Finally, a third difference concerns the real-time requirements:
- Classic SCADA systems without particular real-time requirements. The main function is to acquire information from the process, in order to provide a summary view of the status, promptly report the occurrence of alarms, record all information and generate reports for production or quality managers. The sending of data to the field devices is usually limited to the configuration of the system or the sending of processing recipes; even when SCADA software performs process control functions, it is acceptable that delays of more than one second can occur.
- SCADA systems characterized by strict real time requirements. These are usually systems made up of several microcontrollers connected to each other and to the supervisory PC via a local network, with deterministic operating systems capable of ensuring response times in the order of thousandths of a second. In these cases, we speak more properly of DCS systems, much more expensive both in terms of development costs and operating costs, the use of which is justified only in the case of large plants that require exceptional performance in terms of reliability and safety.
Choice of SCADA Software


The choice of the SCADA software to use depends on various factors, as well as personal preferences, but in general it is conditioned by the complexity of the application to be developed, the required performances, any constraints imposed by the customer and the available budget. It is also necessary to take into account the learning time, which is much longer, the more complex the SCADA software is. In general, we can say that the use of a complex SCADA software is justified when dealing with large-scale systems, with such a high cost as to make the cost of licenses and development times almost irrelevant; in the case of small or medium sized plants and not particularly high cost, it is better to move towards lower cost SCADA software which requires less learning time. Limiting our analysis to the case of a not particularly complex application, with a single supervision PC connected to several field devices without stringent real-time requirements, we list the points to be analyzed in order to choose the most suitable SCADA software:
- Dimensions of the project: the first point to establish is the number of variables to manage (tag), where "tag" means an external variable, ie a variable exchanged with the field devices. The number of tags is important because it affects license choice, system response times and development costs.
- Interface with field devices: it is necessary to verify that the SCADA software supports all communication protocols with field devices. Or, alternatively, that an OPC Server is available to be installed on the PC, in order to allow communication via the OPC protocol.
- Connectivity with other software: check if the application is required to interface with other software such as MES or ERP; in these cases, the interfacing is usually obtained through the OPC UA Server and OPC UA Client protocols.
- Accessibility via browser: request that remote operators can access the server application via browser from fixed (Desktop) or mobile (Smartphone) devices.
- Interfacing with external DBMS: check if the application has to interface with external DBMS (MySQL, ...) to record data tables (Datalogger function) or to interact through particular instructions (API) that allow the execution of generic queries (SELECT, INSERT , UPDATE, …)
- Remote maintenance: possibility for the operator to access remote devices (typically PLCs) using the SCADA as a "bridge", in order to program the remote devices without having a direct connection (fixed IP, DNS or other).
The choice of SCADA software must always be made by balancing the desired performance with the overall costs, both in terms of cost of licenses and learning and development times. The points listed above are not always all necessary and the best performing products are not always the most suitable. Sometimes a less performing product can be more reliable and easier to manage as well as cheaper. Finally, it is always advisable to check the ability and availability of the SCADA software supplier to offer a prompt and appropriate technical support.
SCADA, IoT and Industry 4.0
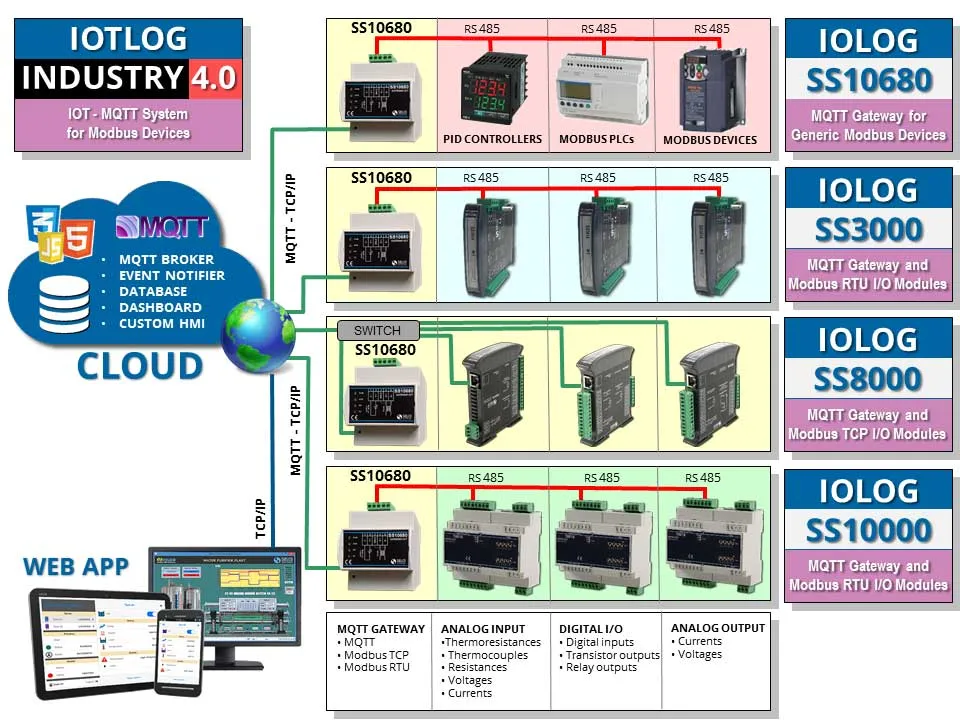

The IoT and IIoT (Internet of Things and Industrial Internet of Things) acronyms indicate all those technologies that make it possible to transform any object, be it a sensor, an actuator, a vehicle or an appliance, into a device connected to the Internet, which is in able to send data to the cloud using light and fast protocols such as MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport).
The increasing trend to use cloud applications has pushed SCADA technologies to evolve towards integration with the Internet of Things. In fact, SCADA systems can increase the potential of the Industrial Internet of Things. By integrating the two technologies, you can get a much faster, more detailed and even more safe collection and verification of company data.
These systems, due to their architecture, are especially suited to manage:
- remote maintenance, remote diagnosis and remote control
- monitoring and control of the working conditions of the machines
- monitoring of energy and water consumption and reduction of emissions
- quality control at the production system level and related processes.
These systems include the key enabling technologies (Key Enabling Technologies - KET's) of Industry 4.0 (SCADA, IoT, cloud, big data, cybersecurity).
More infoExamples of SCADA applications
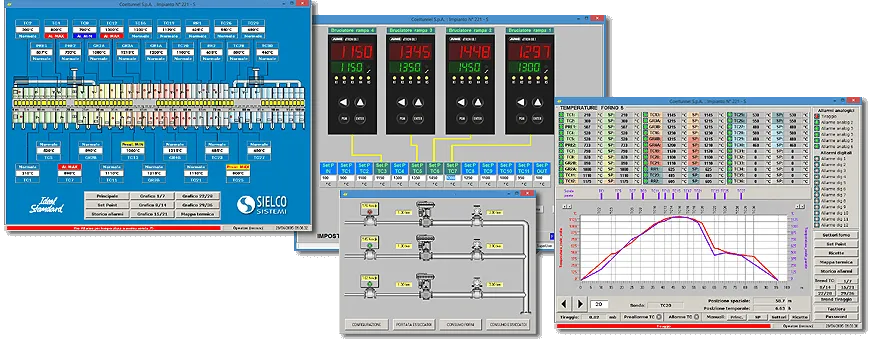

The development of SCADA applications begins within the Industrial Automation, as a response to the request to centralize all the information related to the industrial process in a single control room, with special care to the aspects concerning the good operation of the industrial plant (maintenance and alarm management).
SCADA applications are used in almost all sectors of Industrial Automation, from plastic to wood, from ceramics to food, from textiles to packaging, providing a series of automatic supports aimed at optimizing the production process (quality control, compliance, returns, production reports).
In a short time, SCADA applications go beyond the boundaries of Industrial Automation and are used for remote control of public networks (electrical networks, water networks, railway networks, etc.), for building automation and finally for home automation.
Below is a series of examples of SCADA applications; each example has a link to more information:
- Supervision of low and medium voltage networks: the possibility to select the most suitable contract among different energy providers make more and more convenient a supervisory system able to ensure a continuous monitoring of power consumption and energy costs of low and medium voltage networks.
- Quality control in metal heat treatment: ensures the quality control for heat treatments in a plant division equipped with heterogeneous furnaces (multi-chamber furnaces, pit furnaces, tempering and hardening furnaces), replacing traditional paper recorders and creating production reports.
- Wood stoves test system: allows comparative tests on wood stoves working in different environmental conditions; temperatures are displayed as thermographic maps in order to provide a prompt and effective view of the thermal situation.
- Supervisory control of a spinning plant: makes it possible to produce polypropylene yarns in such a way to guarantee that all product characteristics (torsions, title, tenacity, stabilization, colour, ...) comply perfectly with technical specifications requested by the customer and can be reproduced even after months.
- Monitoring of medical devices with controlled temperatures: it has been installed in many hospitals and research facilities in order to ensure the continuous monitoring of local and remote equipment used for the conservation of organic tissues; the system generates periodic reports for the Quality Certification, in compliance with the current laws.
- Dust pollution level monitoring system: it ensures a continuous monitoring of the level of dust pollution, detected through triboelectric sensors, thus allowing to intervene on the plant before reaching the concentration limit values.
- Supervisory control of a film production plant: the system is applied to a plant for the production of films with a gas barrier, that combines the "cast film” and the "extrusion coating” technologies; it allows to control from a single point the operation of all parts of the multi-stage line, which includes a variety of machines and control equipments.
- Quality control system in food industry: production and storage processes in food industry are subjected to specific laws related to quality control; the system gives the possibility to comply with the requested quality control criteria, limiting both the investment cost and the production loss during installation.
- Supervisory control of ice cream production plant: in order to comply with current rules and protect consumer safety, the system guarantees the quality of the pasteurization process, provides a systematic control on the working status of the mixtures contained in the repining tanks, ensures the effectiveness of cleaning and sterilization.
- Supervisory control of brick and ceramics kilns: it ensures repeatability and production quality by management of production recipes and generation of batch reports; the system displays current and theoretical temperature curves in the continuous kilns, and allows setting of temperature curve and air dilution curve in the intermittent kilns.
- Supervisory control of an automatic installation for heat treating: batch materials are linked to their treatment recipes and positioned on parking platforms; then they are addressed towards carburizing, tempering and hardening heat treatments; an optimizing batch system provides the best sequence to use all the heat treatment elements in a rational and economic way.
- Supervision of plants for wine production: it provides a quality control of all stages of the wine production process, from grapes squeezing to wine bottling: control of fermentation temperature, vacuum concentration, desulphurization, MCR production, tartaric stabilization, must enrichment by osmosis, etc.